攻略:
计算 2 的 38 次方
代码:
#!/usr/bin/env/python |
计算 2 的 38 次方
#!/usr/bin/env/python |
K + 2 = M |
#!/usr/bin/env/python |
查看网页源代码,你就可以看到一堆字符,只要在里面找出 rare characters(出现次数最少的字符)就可以了。
#!/usr/bin/env/python |
一个小写字母两边各站着三个保镖 => 也就是说一个小写字母旁边有且仅有
3 个大写字母
PS:数据在 page source 里面
#!/usr/bin/env/python |
首先根据提示从 linkedlist.html 转到 linkedlist.php,进入 level4
点击图片得到链接:http://www.pythonchallenge.com/pc/def/linkedlist.php?nothing=12345
网页内容为:and the next nothing is 44827
将 44827 替换 12345
得到网页链接:http://www.pythonchallenge.com/pc/def/linkedlist.php?nothing=44827
得到网页内容:and the next nothing is 45439
由此得知本关目的就在于利用程序循环重复以上过程直至得到结果。
中间可能会中断,可以根据提示修正。
#!/usr/bin/env/python |
今天在 Ubuntu 下面安装 GoAgent 遇到出现“the site"s security certificate is not trusted”的问题,根据提示发现是证书错误造成的,解决方法如下。
1)安装 libnss3-tools
sudo apt-get install libnss3-tools |
2)导入证书
certutil -d sql:$HOME/.pki/nssdb -A -t TC -n "goagent" -i your_goagent_directory/local/CA.crt |
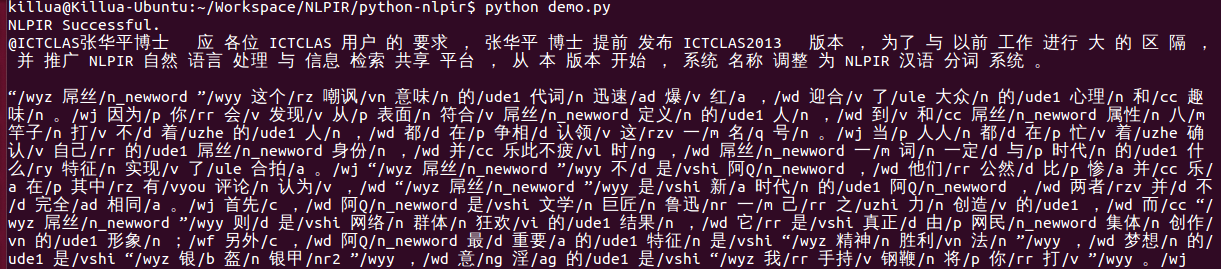
本文只适用于 python-nlpir V1.0 版本,有关 V2.0 版本详情参照项目源代码。
python-nlpir 是 NLPIR 中文分词工具的 Python 封装,利用 SWIG 完成 C++到 python 的接口转换。
项目地址:https://github.com/zhenlohuang/python-nlpir
NLPIR 汉语分词系统(又名 ICTCLAS2013),主要功能包括中文分词;词性标注;命名实体识别;用户词典功能;支持 GBK 编码、UTF8 编码、BIG5 编码。新增微博分词、新词发现与关键词提取;是当前最好的中文分词工具之一。
SWIG 是个帮助使用 C 或者 C++编写的软件能与其它各种高级编程语言进行嵌入联接的开发工具。SWIG 能应用于各种不同类型的语言包括常用脚本编译语言例如 Perl, PHP, Python, Tcl, Ruby and PHP。支持语言列表中也包括非脚本编译语言,例如 C#, Common Lisp (CLISP, Allegro CL, CFFI, UFFI), Java, Modula-3, OCAML 以及 R,甚至是编译器或者汇编的计划应用(Guile, MzScheme, Chicken)。SWIG 普遍应用于创建高级语言解析或汇编程序环境,用户接口,作为一种用来测试 C/C++或进行原型设计的工具。SWIG 还能够导出 XML 或 Lisp s-expressions 格式的解析树。SWIG 可以被自由使用,发布,修改用于商业或非商业中。
%module NLPIR |
swig -c++ -python NLPIR.interface |
执行完成接口转换后,将生成 NLPIR_wrap.cxx、NLPIR.py 两个文件,到目前为止已经完成了接口的转换,不过现在接口还不能使用,因为还没有编译好相应的库。
''' |
sudo cp libNLPIR.so /usr/lib |
由于原来的 NLPIR.h 在 gcc
编译器中的兼容性并不好,所以需要对原来的头文件进行简单的修改。
将
#ifdef OS_LINUX |
改为
#ifdef linux |
将
#ifdef OS_LINUX |
改为
#ifdef linux |
python setup.py build_ext --inplace |
为了方便使用对生成的 NLPIR.py 进行重封装。
#!/usr/bin/env python |
#!/usr/bin/env python |
参见:http://www.yidooo.net/archives/unable-to-find-vcvarsall-bat-solution.html
Windows:将 NLPIR.dll copy 到 System32 下
Linux:将 libNLPIR.so copy 到/usr/lib 或者/usr/lib64 下
请参考:http://ictclas.nlpir.org/newsDetail?DocId=386
Date: 2013-11-15
Version 1.1: 感谢zzdwcm,所提供有关 Linux 64bit 的补丁。
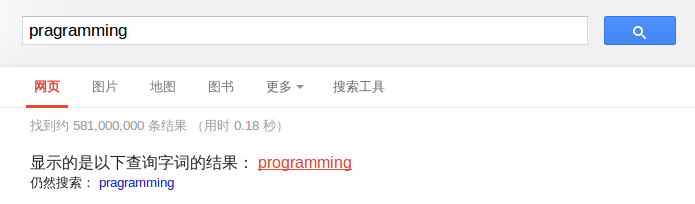
所谓拼写检查,就是在使用 Google 的时候,输入错误的时候,系统对其自动纠正,如下图所示:
目前有很多方法可以实现这样的技术,这里使用的是贝叶斯推断的方法。
有关贝叶斯推断的相关理论和背景知识,可以参考<href="http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2011/08/bayesian_inference_part_one.html>贝叶斯推断及其互联网应用(一):定理简介
用户输入了一个单词。这时分成两种情况:拼写正确,或者拼写不正确。我们把拼写正确的情况记做 c(代表 correct),拼写错误的情况记做 w(代表 wrong)。
拼写检查,就是在发生 w 的情况下,试图推断出 c。从概率论的角度看,就是已知 w,然后在若干个备选方案中,找出可能性最大的那个 c,也就是求 P(c|w)的最大值。根据贝叶斯定理:P(c|w) = P(w|c) _ P(c) / P(w)对于所有备选的 c 来说,对应的都是同一个 w,所以它们的 P(w)是相同的,因此我们求的其实是 P(w|c) _ P(c)的最大值。
P(c)的含义是,某个正确的词的出现"概率",它可以用"频率"代替。如果我们有一个足够大的文本库,那么这个文本库中每个单词的出现频率,就相当于它的发生概率。某个词的出现频率越高,P(c)就越大。
P(w|c)的含义是,在试图拼写 c 的情况下,出现拼写错误 w 的概率。这需要统计数据的支持,但是为了简化问题,我们假设两个单词在字形上越接近,就有越可能拼错,P(w|C)就越大。举例来说,相差一个字母的拼法,就比相差两个字母的拼法,发生概率更高。你想拼写单词 hello,那么错误拼成 hallo(相差一个字母)的可能性,就比拼成 haallo 高(相差两个字母)。
所以,我们只要找到与输入单词在字形上最相近的那些词,再在其中挑出出现频率最高的一个,就能实现 P(w|c) * P(c) 的最大值。
这里使用的是http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/Wiktionary:Frequency_lists#English语料库,该语料库是这是一个由志愿者编纂的多语言词典计划,它旨在囊括各种语言词汇的语源、读音和解释。任何人甚至无须登录就可以编辑任何字词。在源代码中使用的 wiktionary 文件,里面每一行为一个单词以及单词的频率,格式为:word:frequency。
DICTIONARY = {} |
这里计算相似单词使用的是编辑距离的方法,所谓编辑距离,两个单词通过删除、交换、更改和插入四种操作中的一种,就可以让一个词变成另一个词。这里生成编辑距离为 1 的单词集
def generate_edit_distance1_words(word): |
根据 step 2 所得到的候选单词集,在字典中进行比较,得到概率最大作为拼写建议。
def words_filter(words): |
python spelling_corrector.py pragramming |
#!/usr/bin/env python |
完整代码可以参见 github:https://github.com/zhenlohuang/spelling_corrector
不足之处
拼写检查的精度很大程度依赖所使用的语料库,而且本文仅仅只是抛砖引玉,只考虑编辑距离为
1 的单词的情况。许多情况下单词的拼写错误不只一处。
http://norvig.com/spell-correct.html
http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2012/10/spelling_corrector.html
http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/Wiktionary:Frequency_lists#English
PySide 是跨平台的应用程式框架 Qt 的 Python 绑定版本 。在 2009 年 8 月,PySide 首次发布。提供和 PyQt 类似的功能,并相容 API。但与 PyQt 不同处为使用 LGPL 授权。
安装命令:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:pyside |
如果想只装某个模块:
sudo apt-get install python-pyside.qtgui |
1)引用计数算法(Reference Counting)
给对象中添加一个引用计数器,每当一个地方引用它时计数器+1,;当引用失效时,计数器-1;任何时刻计数器为
0 的对象就是不可能再被使用。
举例:Python,Flashplayer,COM
缺陷:无法解决对象之间的循环引用问题。
2)根搜索算法 以 GC Roots
作为起点,从这些节点开始向下搜索搜索所走过的路径称为引用链(Reference
Chain),当一个对象到 GC Roots
没有和任何引用链相连(也可以理解为图论中的该节点不可达),则该对象是不可用的。
Java 中,可以作为 GC Roots 的对象包括:
①Stack 中(Stack Frame 的本地变量表)中的引用对象。
②Method Area 中的静态属性引用对象和常量引用对象。
③Native Method Stack 中 JNI 的引用对象。
1)强引用(Strong Reference):类似“Object obj=new
Object()”这类的引用,只要强引用存在 GC 就不会收回被引用的对象。
2)软引用(Soft
Reference):对于软引用的对象,在系统将要发生内存溢出之前,将会把这些对象列进回收的范围,进行第二次回收。如果还没有足够的内存,就会抛出内存溢出异常。
3)弱引用(Weak
Reference):被弱引用关联的对象只能保留到下一次垃圾回收发生之前。
4)虚引用(Phantom
Reference):被虚引用的对象,完全不会影响其生存时间构成,也无法通过虚引用取得一个实例。虚引用的唯一目的就是在对象被
GC 回收时可以收到一个通知。
1)标记-清除算法
首先标记出所有需要回收的对象,在标记完成后统一回收掉所有被标记的对象。
优点:简单
缺点:效率低下,且容易产生不连续的区域
2)复制算法 将内存空间分为 Eden 和 Survivor
两块区域,当一块区域内存用完时,将存活的对象复制到另一块区域,然后把之前的区域清理掉。
优点:简单高效,不会产生不连续的区域
缺点:内存利用率只有 50%
3)标记-整理算法
相比标记-清除算法,在标记之后并不马上进行回收,而是将存活的对象向一端移动,然后清理掉端外内存。
4)分代收集算法 将 Java Heap 分为新生代(Younger
Generation)和老年代(Tenured
Generation),根据各个年代的特点采用最适合的收集算法。